There are so many different graphic file formats and image options available, you may be confused about what they are, how they work, and how they can be used efficiently to display images and graphics across different platforms.
This article is a quick overview to help you understand which types of files are best for common graphics like photos, logos, and other graphics displayed on the web and used in printed collateral.
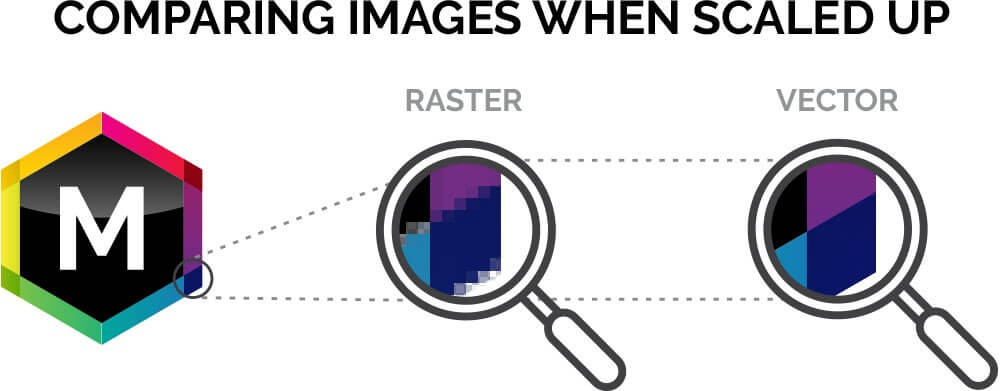
What Is the Difference Between Raster and Vector Images?
There are two types of digital graphic files—raster and vector. Raster graphics are composed of a combination of pixels, but vector graphics are composed of paths and are based on mathematics so that they can easily scale larger or smaller.
This is a highly simplified summary, so let’s explore raster and vector graphic files in more detail.
What Is a Raster Image?
Raster images are made up of tiny squares of colors or shades of black called pixels. When magnified enough, you can see the individual pixels of the image and that each one is a single color. When all those pixels are viewed as a whole, they work together to form a rich, detailed image with intricate color variations and soft gradients.
Digital photographs you see on a website, pictures you take with your phone or digital camera, or scanned artwork are all raster images. Because of the amount of digital information contained in a raster image in all those little pixels, file sizes tend to be larger than those of vector graphics.
What Is a Vector Image?
Vector graphics are built mathematically and are made up of points and paths. Generally, vector graphics are less detailed containing fewer gradients and less diversity of color. And, even though they can be used to form nearly photo-realistic graphics, they tend to be used in building graphics with more uniform, solid colors and fewer details.
Vector graphics are commonly used to produce logos and other simpler graphics that may need to be used at different sizes and have the benefit of maintaining crisp, sharp edges, even when they are enlarged greatly.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Common Raster Formats?
Raster images are extremely versatile and are the preferred format when realistic, photographic-type imagery is desired.
Want to generate more leads with your design? Get your free brand style guide sample today!
When you take a photograph on your phone or digital camera, a raster image is automatically generated every time you tap the shutter icon. They can be displayed on any common electronic device, shared through email and text messages, and posted to social media sites such as Facebook, Twitter, or Instagram.
Raster files can also be used to print photographs or in any piece of printed collateral such as a brochure, poster, or magazine. Creating raster images doesn’t require any special software knowledge or training, and they are easily produced by anyone that can use a smart phone or camera.
Many different raster file types can be displayed on the internet — with JPGs, PNGs, and GIFs being the most common. Each one contains advantages and disadvantages over the others.
JPG Raster Files
JPGs are the most commonly used graphic files on the web because of their ability to display millions of colors with photographic quality at low file sizes. These lower file sizes allow websites to load and display quickly, which is crucial in today’s mobile-friendly world. Most digital cameras and smart phones save pictures as JPGs as the default format.
One disadvantage of the JPG is that they are “lossy,” meaning each time they are opened in a photo editing software and re-saved, they lose some graphical information, and jagged edges or pixelated areas can appear on close examination, especially when opened and resaved multiple times.
PNG Raster Files
PNGs also deliver photographic quality but are generally larger and slower loading on web browsers than JPGs — But PNGs are lossless when edited and resaved.
The biggest advantage of a PNG over a JPEG is the ability to have transparent (see-through) areas saved in the file. This is especially useful when placing the PNG over another color or graphic where you want the background to show through.
GIF Raster Files
GIFs are also lossless, but the main advantage of GIF files is that they can be animated. However, they are limited to a display of 256 index colors and are best used for smaller, more simple graphics and animations.
TIF Raster Files
Another widely-used raster file type is the TIF, most commonly used in the graphics and print industry. TIFs have all of the full-color display ability of JPGs, but they are lossless. TIFs can also contain editable layers and transparent areas when needed.
What are the benefits and disadvantages of different vector formats?
Because vector images use mathematical equations and are generally less detailed than raster images, they are usually smaller in size. Therefore, vector files are easier to distribute through email and take up less space on your computer.
While hard drive space may not be as much of an issue today as in the past, because of the easy availability of external hard drives and SSDs (solid-state drives), the main benefit of a vector image is the ability to resize it without the degradation, or pixelation, that occurs to raster images when they are increased in size.
You should avoid using raster images to create a logo for this very reason. When creating a logo or illustration, a vector format is the best option, because it allows you to use the graphic at any size with no loss of image quality. This is quite important for using your logo across many different platforms, both digital and print.
One disadvantage of vector graphics is on the production side. To produce a vector graphic, some basic knowledge and software training is usually necessary — it’s not as easy as pressing a shutter icon on your smart phone. There are many vector creation and editing apps available, but Adobe Illustrator is the industry standard for creating vector graphics and has been the leader in this area for graphic design professionals for many years.
Another disadvantage of vector graphics is that most are not compatible with internet browsers— except for the SVG. The SVG is a very versatile vector file format that can be used on the web. SVGs support transparency, can be animated, and maintain all of other benefits of vector formats, including clarity at any size and resolution.
Other common vector formats such as EPS, AI, and some PDFs are used in the printing industry — most commonly for logos and other simple graphics.
Takeaway for Raster and Vector Images
Using and producing the right file formats at the right sizes can help save time and avoid unwanted issues in both digital and printed materials. Avoiding problems with compatibility, download speed, and print quality will help your business get its message in front of your audience with the efficiency and quality your products and services deserve.
Are you searching for Austin graphic design firms or Houston graphic designers that knows how to leverage the right design tools and consistently provide you with the best value?
At MARION, we take design seriously, and we know our way around file types. You can trust the experts at our Houston marketing agency to use the absolute best practices when it comes to efficient and effective use of the right raster and vector images when creating beautiful graphics for your business.
Contact us online today or call us at (713)-568-4826 to learn how we can help you design and create something special to help your business look its best.